Managing Back Pain: Practical Steps for Relief
Introduction to Back Pain
Back pain is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide, interfering with daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes and exploring effective treatment options is crucial for managing this condition. Whether it’s a result of poor posture, an injury, or a chronic condition, addressing back pain requires a comprehensive approach.
Understanding the Causes of Back Pain
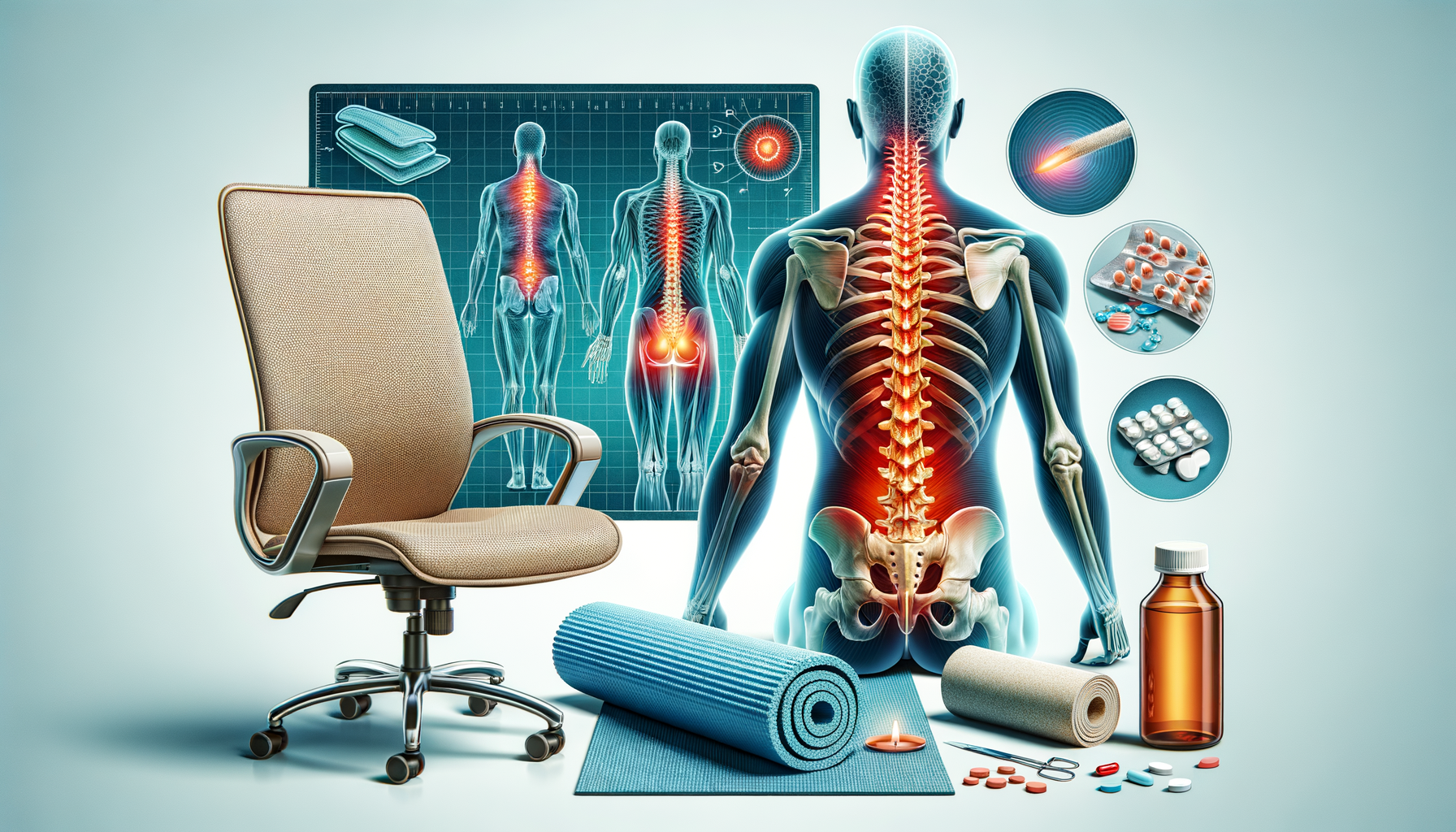
Back pain can arise from various factors, including muscle strain, herniated discs, or degenerative diseases. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective treatment. Common causes include:
- Muscle or ligament strain due to heavy lifting or awkward movements.
- Bulging or ruptured discs that press on nerves.
- Arthritis leading to narrowing of the space around the spinal cord.
- Osteoporosis, resulting in fractures or weakened bones.
Each cause requires a tailored approach to treatment, emphasizing the importance of professional diagnosis and personalized care.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For many, non-surgical treatments offer significant relief from back pain. These methods focus on reducing pain and improving function without invasive procedures. Common non-surgical options include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Chiropractic care to adjust misalignments in the spine.
- Acupuncture for pain relief and muscle relaxation.
- Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants.
These treatments can be highly effective, especially when combined with lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In cases where non-surgical methods fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery is typically considered when there is severe pain, nerve compression, or structural problems that impair mobility. Common surgical procedures include:
- Discectomy, which involves removing a portion of a herniated disc.
- Laminectomy, aimed at relieving pressure on the spinal cord by removing part of the vertebra.
- Spinal fusion to stabilize the spine by joining two or more vertebrae.
While surgery can be effective, it is often reserved for severe cases due to the risks and recovery time involved.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Adopting preventive measures and making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of back pain recurrence. Key strategies include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the spine.
- Engaging in regular exercise to strengthen core muscles.
- Practicing good posture, especially during prolonged sitting or standing.
- Using ergonomic furniture and equipment to support the back.
Incorporating these habits into daily life can help maintain spinal health and prevent future episodes of back pain.
Conclusion: Tailoring the Approach to Individual Needs
Managing back pain effectively requires a personalized approach that considers the individual’s specific condition and lifestyle. By combining medical advice with practical lifestyle adjustments, individuals can achieve significant relief and improve their quality of life. Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Remember, the path to relief is often multifaceted, involving both medical interventions and proactive self-care.